This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
QGIS Real World Data Tutorial
ArmA 3 QGIS Real World Data Tutorial By Ross
This process has often been described using Global Mapper, but I wanted to detail the equivalent steps within the open source GIS app QGIS.
The goal is to achieve an export image with the same or better quality than would be possible with Global Mapper.
The is my second revision of this process as I recently discovered that due to an update to GDAL (2.4.0) one of the key steps in the original tutorial using 'Clip Raster by Mask Layer' no longer works perfectly!
So I reworked the process by getting a bit more under the hood, and using GDAL command line where possible, this also simplifies the process a little and reduced even further processing on the data.
Using following versions:
First an overview of the steps required:
For Heightmap:
- Load heightmap into QGIS (drag and drop)
- Set QGIS to appropriate CRS for location of your HM
- Create shapefile & generate square feature using Advanced Digitizing panel
- Obtain extents from square feature
- Run 2 GDAL commands
- First to set cell size, CRS and then clip to shapefile square extents
- Second to convert to .asc file
For Satellite image
For single tile export
- Load in just the .map files into QGIS
- Merge Rasters
- Obtain extents from square feature
- gdalwarp command will set cell size, CRS and then clip to shapefile square extents
For 4 tile export
- Load in just the .map files into QGIS
- Merge Rasters
- Create grid – 2 x 2 Feature
- Move each quarter to its own shapefile layer
- Obtain extents from each quarter feature
- Run gdalwarp command for each quarter to set cell size and CRS and clip to shapefile square feature extents
And now detailed steps for:
Heightmap:
Drag and drop your heightmap '.asc' into QGIS
Set QGIS to appropriate CRS for location of your HM
Clicking on the CRS section bottom right within QGIS – will bring up the Project Properties for CRS
Select the CRS to match your real world data, in this example its ‘WGS 84 UTM zone 20N’ because the terrain is from the Montserrat in the Caribbean. See also UTM projection.
This will ensure your QGIS project space works appropriately with any other data you want to add - eg road shapefiles etc. Terrain Builder will only use UTM 31N but we'll get to that later.
Create shapefile & generate square feature using Advanced Digitizing panel
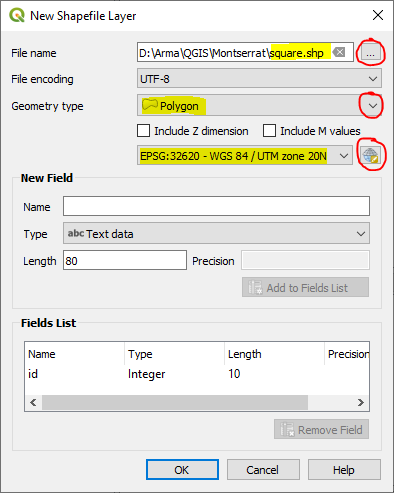
Top menu – Layer > Create Layer > New Shapefile Layer
Save to project folder location
Change Geometry type to ‘Polygon’
Match CRS so it is the same as that just configured in above step
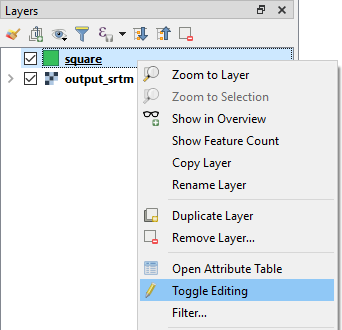
Right click on your shapefile in layers window & select ‘Toggle Editing’
From menu – View → Toolbars → Advanced Digitizing Toolbar
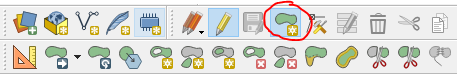
Select ‘Add Polygon Feature’
Select Enable advanced digitizing tools
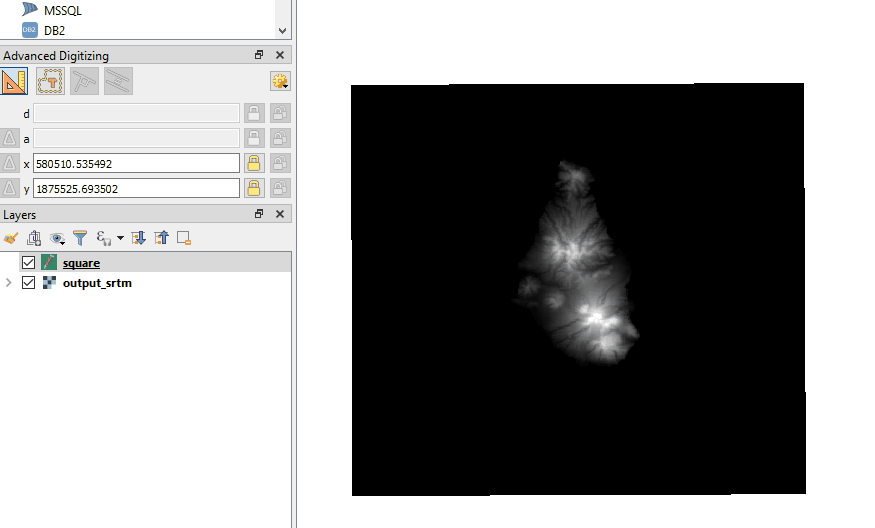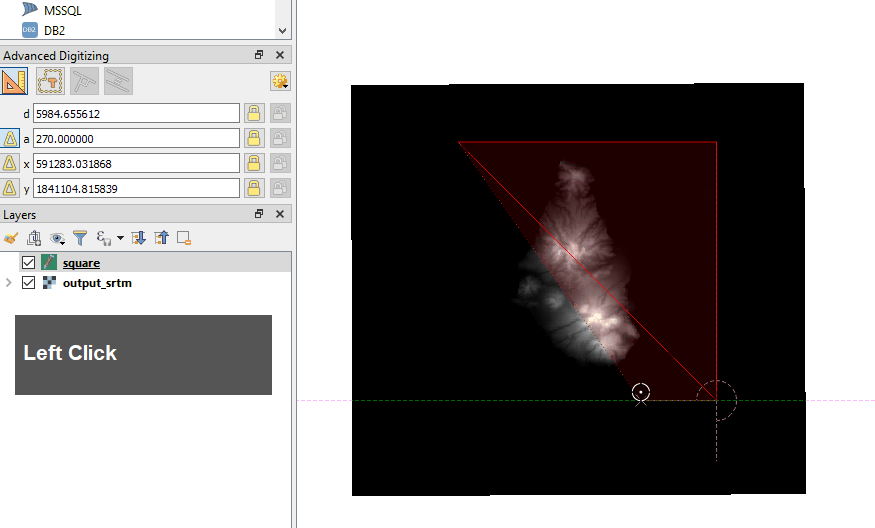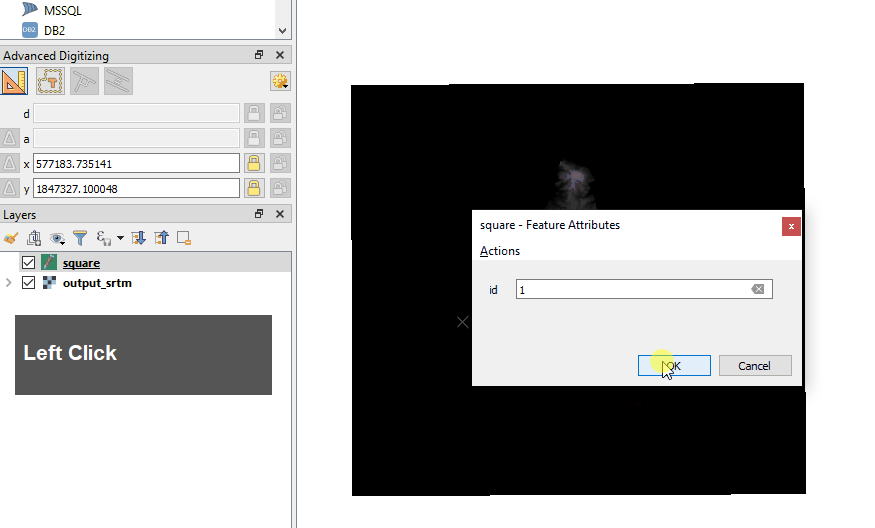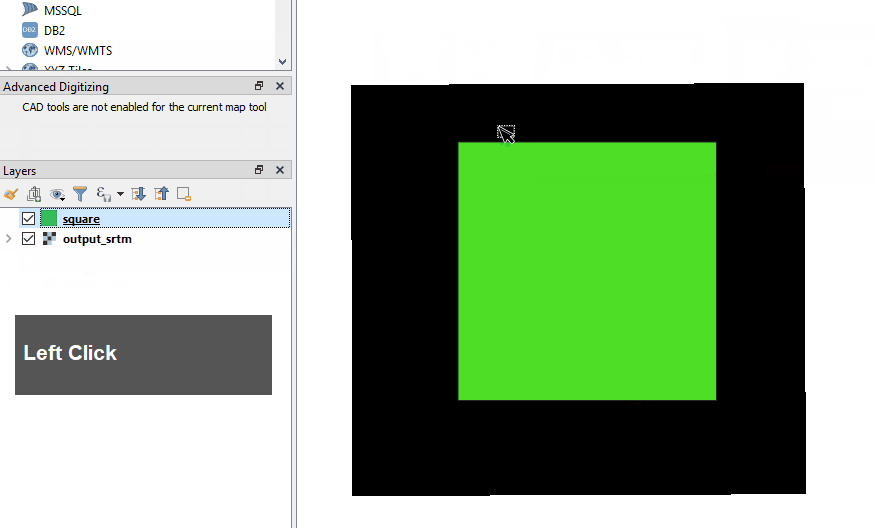
To create a perfect square, left mouse click for your top left starting point, move your mouse to the right a little, then press ‘d’ on keyboard, type in the exact width (distance) required (in this example ‘20480’) then immediately press Enter – be careful not to move the mouse before pressing Enter or it will mess up the number. Press left mouse click and you will have drawn your first horizontal line which turns red. By default this tool snaps to 90 degree angles, making it easy to draw your lines. Now to draw the vertical line start moving mouse your down, press ‘d’ again and type in same figure as above, press Enter and another left mouse click, repeat the process for the last 2 lines of the square.
See a short video example using the Advanced Digitizing tool:
After the last left mouse click from the step above, the tool is still waiting to plot more points, so to finalise the square do a right mouse click
This will then bring up a dialogue – just type any number and Enter
Obtain extents from square feature
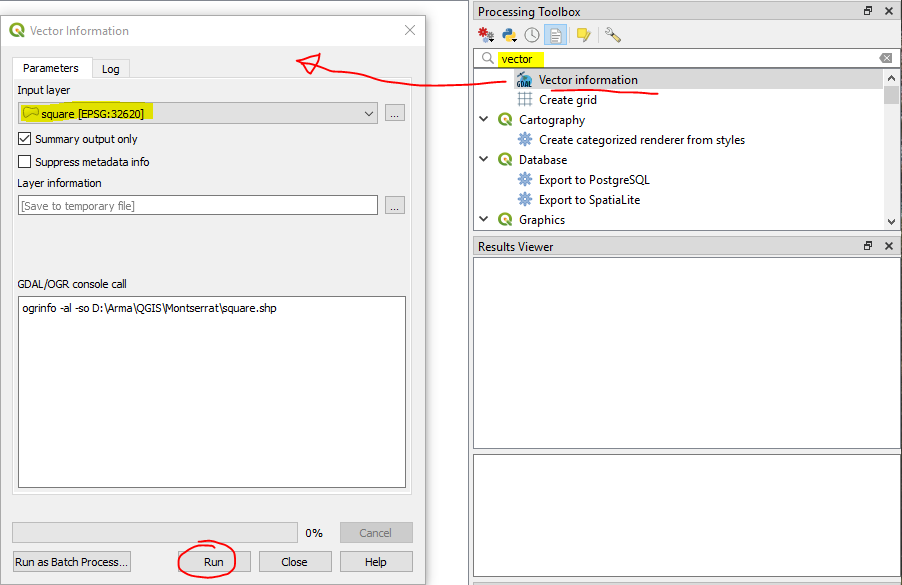
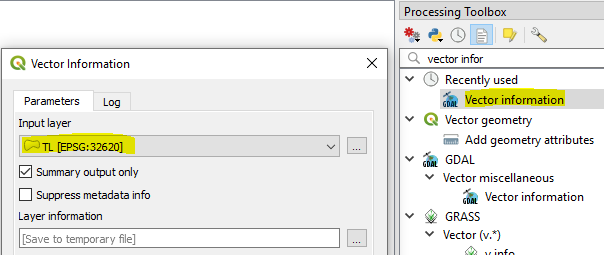
Activate the toolbox if it is not already available
Start typing 'vector' in Processing Toolbox search bar, and you will see 'Vector information'
Double click it and make sure your square input layer is selected - then just click Run
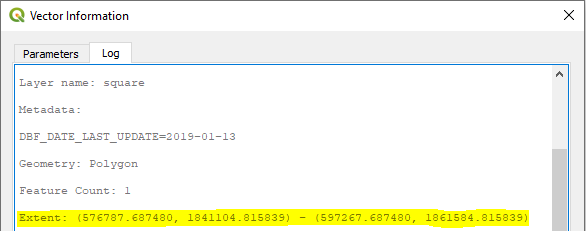
You will only need to copy the Extent figures, which we will use within the GDAL commands in the next step
Run the first GDAL command to set CRS, cell size and then clip to shapefile square extents
From menu - Plugins > Python Console
Click 'Show Editor'
The blank window on the right is where you will enter GDAL commands
Now you are ready to edit the command below to match your data - sections in bold are the parts to edit:
import os
os.system(r'''gdalwarp -t_srs EPSG:32620 -wo SOURCE_EXTRA=1000 -tr 5.0 5.0 -srcnodata “-9999” -r cubic -of GTiff -te 576787.687480 1841104.815839 597267.687480 1861584.815839 D:/Arma/Heightmaps/Opentopo/output_srtm.asc D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/converted.tif''')
Some explanation of the key parameters:
-t_srs EPSG:32620
CRS to match where the heightmap is from in the world.
-tr 5.0 5.0
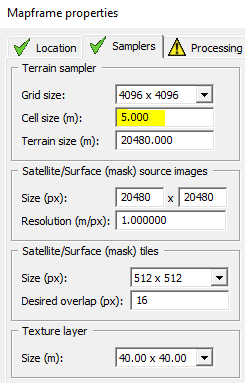
The desired resolution of your heightmap, match with Cell size set within your Mapframe properties in Terrain Builder:
-te 576787.687480 1841104.815839 597267.687480 1861584.815839
The 4 long figures represent the extents of your square, and should be replaced with your own figures obtained in previous step.
Update the paths to match where you are storing your source heightmap, and where you want the output tif saved to.
Input:
D:/Arma/Heightmaps/Opentopo/output_srtm.asc use double quotes around your input path if it contains any blanks
Output:
D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/converted.tif
Run second GDAL command - converting tif from above step to a Terrain Builder friendly .asc
import os
os.system(r'''gdal_translate -of AAIGrid D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/converted.tif D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/final.asc''')
Satellite image
For single tile export
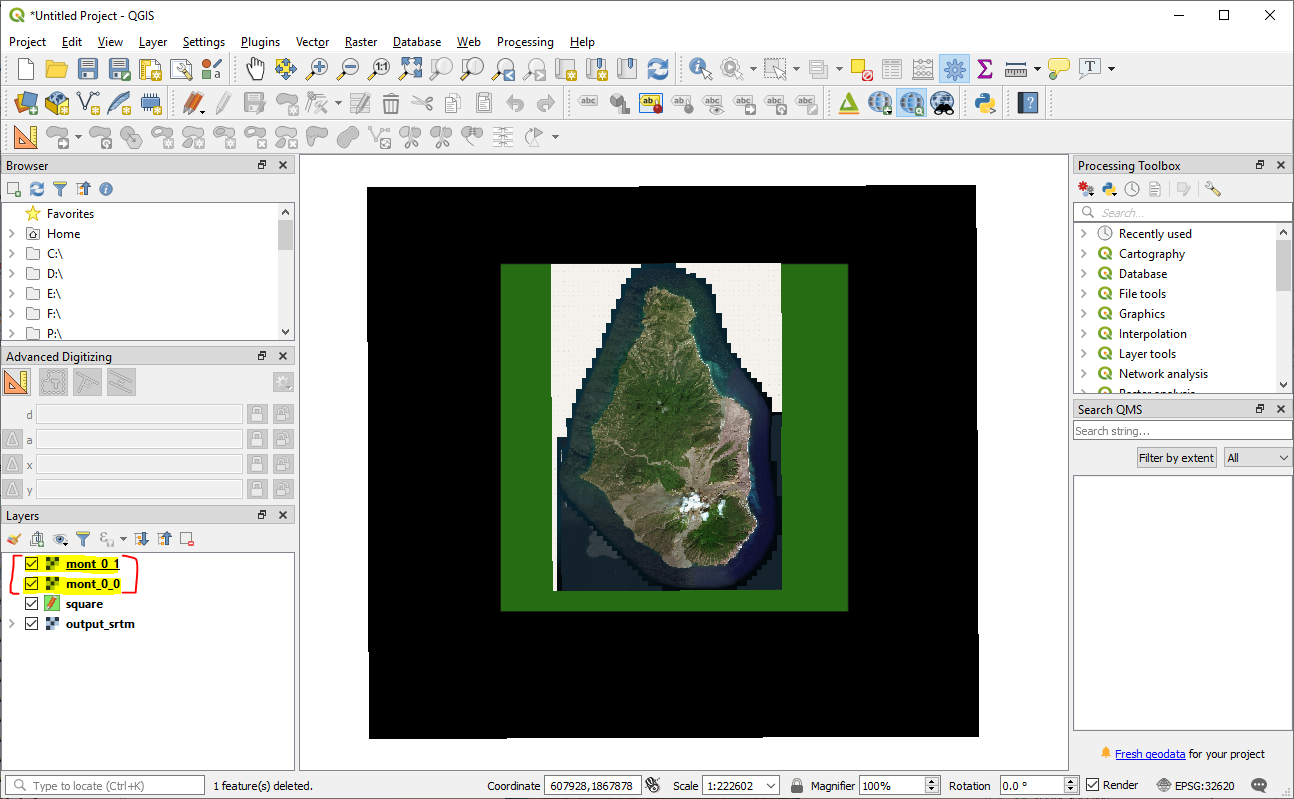
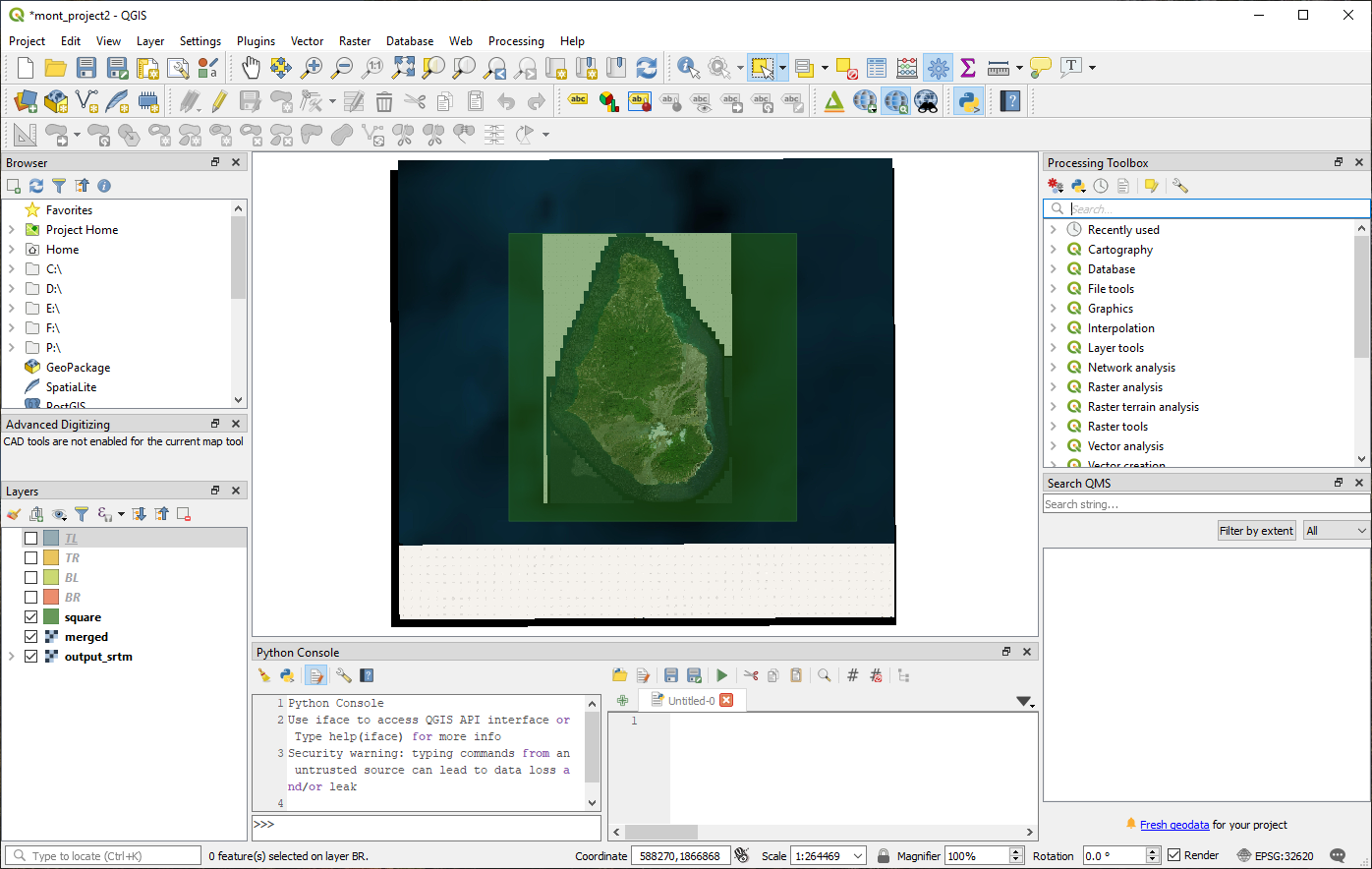
Load in just the .map files into QGIS
Merge Rasters
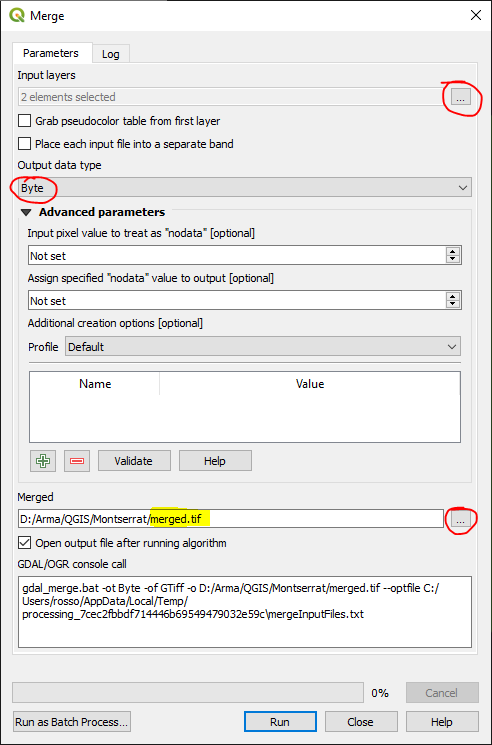
Top Menu - Raster → Miscellaneous → Merge
Select all your .map files as input layers
change Output data type to ‘Byte’ as the default is ‘Float32’.
Select ‘Save to File’ under Merged – as the default is to a temporary file.
Obtain extents from square feature
You should already have this from working on heightmap above 576787.687480 1841104.815839 597267.687480 1861584.815839
Run GDAL command
import os
os.system(r'''gdalwarp -t_srs EPSG:32620 -r cubic -wo SOURCE_EXTRA=1000 -tr 1.0 1.0 -r cubic -of BMP -te 576787.687480 1841104.815839 597267.687480 1861584.815839 D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/merged.tif D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/mont.bmp''')
Some explanation of the key parameters:
-t_srs EPSG:32620
Sets the CRS
-tr 1.0 1.0
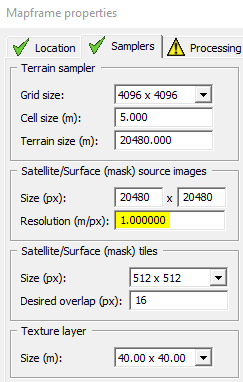
Sets the resolution of your satellite image to 1mtr per pixel - which is recommended. Make sure it matches your settings within Terrain Builder.
-te 576787.687480 1841104.815839 597267.687480 1861584.815839
Clips to shapefile square extents
For 4 tile export
Detailing additional steps required for a 4 tile export – which would suit those terrains that are 40960px x 40960px and higher.
Load in just the .map files into QGIS
Merge rasters - same as above (single tile export)
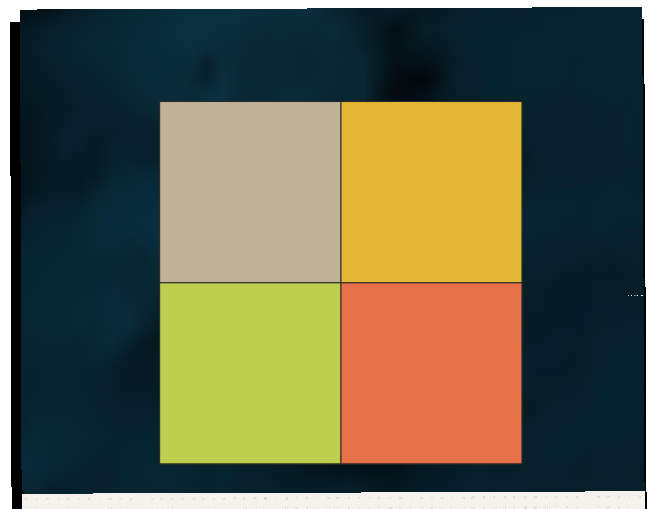
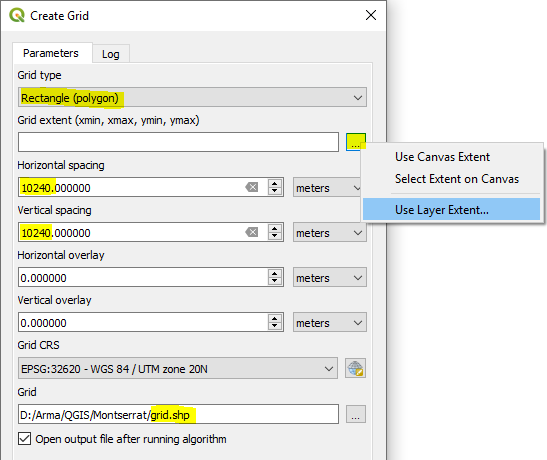
Create grid – 2 x 2 Feature
You will need to have created the square shapefile first – see above steps
Top Menu – View → Panels → Processing Toolbox
Processing Toolbox Menu – Vector Creation > Create Grid
Set Grid type to ‘Rectangle (polygon)’ & the Horizontal & Vertical to half the distance of your main square
Set it to save new grid feature to .shp file
Select the shapefile layer for your square
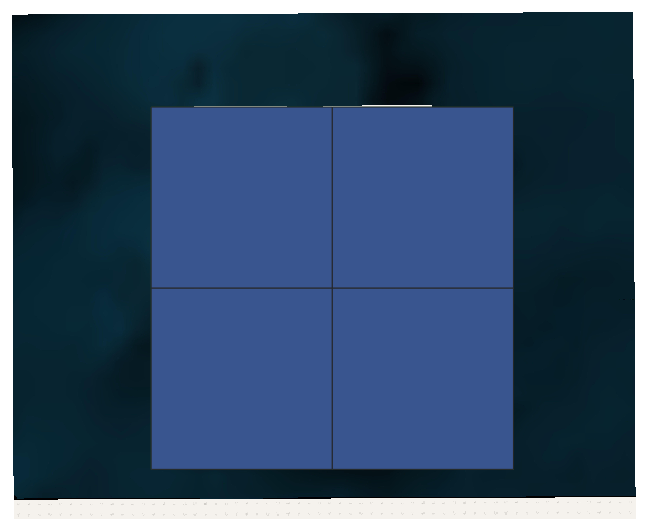
After clicking Run, your original square will then be Covered with a new grid of 4 tiles – perfect quarters of your original square
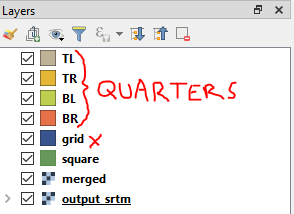
Move each quarter to its own shapefile layer
Because you will need to export each quarter separately for use in Terrain Builder, we will move each quarter onto its own shapefile layer.
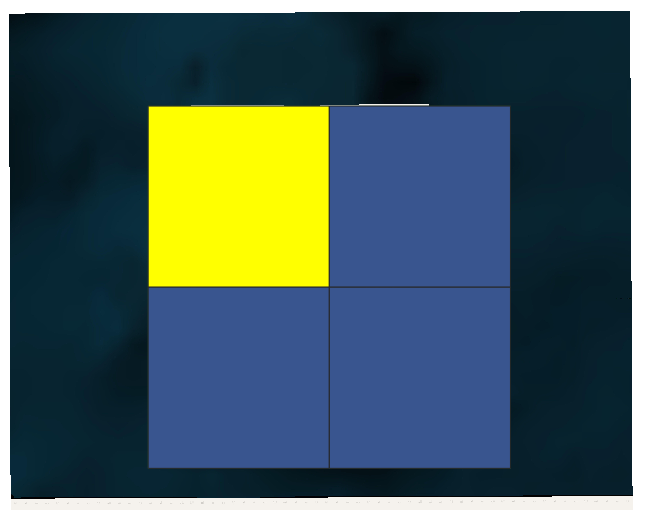
Click Select Features -
And select the first quarter:
Top Menu – Edit > Copy Features
Then… Edit → Paste Features As → New Vector Layer
Save shapefile layer to something obvious
I’ve used ‘TL’ for top left.
Repeat for the remaining quarters and you’ll have something like below, ‘Grid’ can be deleted.
You will then have 4 tiles which we can use to gather each quarters extents
Obtain extents from each quarter feature
Copy extents to clipboard
And list them out for safe keeping -
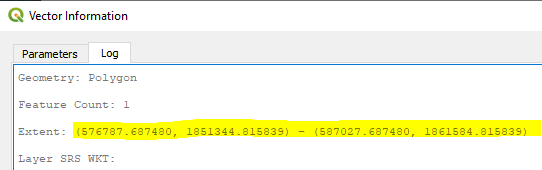
TL - Extent: (576787.687480, 1851344.815839) - (587027.687480, 1861584.815839)
TR - Extent: (587027.687480, 1851344.815839) - (597267.687480, 1861584.815839)
BL - Extent: (576787.687480, 1841104.815839) - (587027.687480, 1851344.815839)
BR - Extent: (587027.687480, 1841104.815839) - (597267.687480, 1851344.815839)
Run GDAL command for each quarter to set cell size and CRS and clip to shapefile square extents
import os
os.system(r'''gdalwarp -t_srs EPSG:32620 -r cubic -wo SOURCE_EXTRA=1000 -tr 1.0 1.0 -r cubic -of BMP -te 576787.687480 1841104.815839 597267.687480 1861584.815839 D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/merged.tif D:/Arma/QGIS/Montserrat/TR.bmp''')
Loading your assets into Terrain Builder
Heightmap (.asc) edits
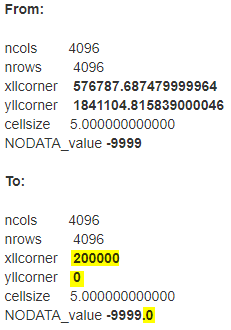
Open your asc and change the following:
Before loading the asc file into Terrain Builder, delete the .prj file. Otherwise it will not import into TB.
Satellite image
Before loading the satellite image into Terrrain Builder delete the .bmp.aux file
Managing the project assets within QGIS
Save your QGIS project so that you can return to export further data at a later date.
Layers can be tidied up to hold the essentials ready for the next time you want to re-run GDAL commands, or export anything else like road shapefiles or mask layers etc.
Coming Soon:
- Road shapefile creation
- Assisted image classification - for creation of mask
- 3d preview using Qgis2threejs